OEE Forumula & Calculation for various Manufacturing Process
by Saravana Kumar

In manufacturing, enhancing production is a continuous and essential endeavor. Even a small improvement in production line efficiency can translate into significant revenue gains. During this optimization journey, you might encounter the term Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE). So, what role does OEE play in evaluating productivity? The method for calculating OEE can vary based on the specific manufacturing process, as each process has unique cycle times, production yields, and efficiency metrics. In this article, we’ll explore various manufacturing processes, explain methods of calculating OEE, and detail how OEE is determined for different types of production systems. In manufacturing, enhancement of production is an endless undertaking. In any case, a commendable one.
The manufacturing process covered for the OEE calculation example includes
- Discrete manufacturing
- Continuous process
- Batch process
- Repetitive manufacturing
- Job shop manufacturing
The nature of the manufacturing process and the method of material handling are crucial factors that significantly impact the parameters used in calculating OEE. It's essential to thoroughly understand the specific process before determining and applying the appropriate OEE formula.
Discrete Manufacturing
Discrete manufacturing is a method in manufacturing process that creates distinct and countable products. The products can be individually identified and tracked. The production can be done in individual pieces or batches which can be disassembled when needed. The key characters of the process is distinct & identifiable, variety & customizable, assembly production and flexiblity. Some of the products that fall under the discrete process are cars, electronics, furniture, smart phones and home appliances.
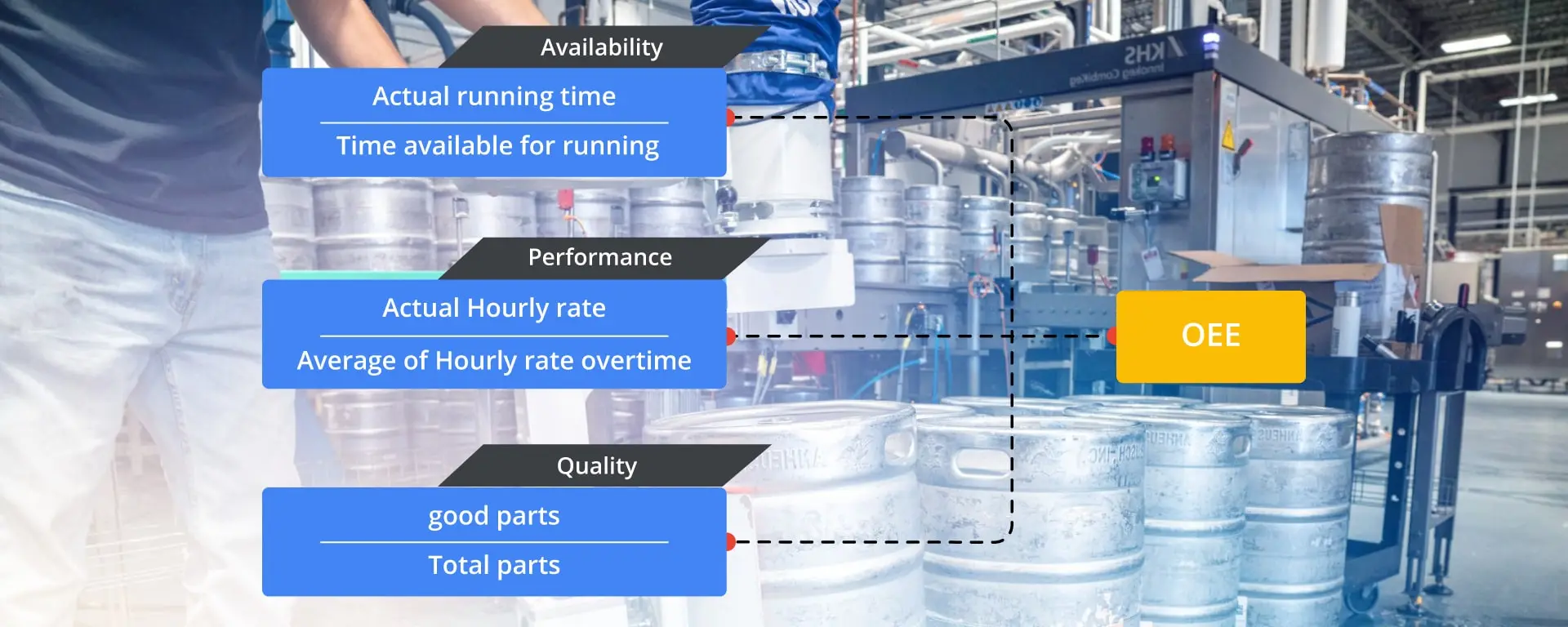
How to Calculate OEE?
The OEE Formula for the Discrete manufacturing process is simple more like the process encampassing the three basic KPIs of availability, performance and the quality of the parts produced. Manufacturing Execution System provides all the necessary data to track the OEE from time to time.
- Availability – The comparison of the time for which the machine is available for operation against the time for which the machine is actually running for production.
- Performance – Actual output versus what the machine should have produced for the time it is actually running.
- Quality – The total number of parts manufactured against the number of parts produced according to the client’s specifications ( at the right quality standards).
Availability = Runtime / Planned production time
Performance = (Ideal cycle time * Total count) / Runtime
Quality = Quantity of good parts / Total quantity made
OEE = Availabilty * Performance * Quality (* given in percentage*)
Continuous Manufacturing
Continuous manufacturing is the process in which the raw materials are fed into the system and the finished product will be produced without any interruption. Unlike discrete manufacturing where partial parts can be produced in different process, continous manufactuirng has no stoppages in between. The process as well runs non stop and has higher capacity to produce large quanitites of standard products.
Industries such as chemicals, oil & gas, pharmaceuticals, paper, steel, and food production commonly use continuous manufacturing. In these processes, raw materials flow through a series of automated steps, with each phase seamlessly connected to the next to maintain efficiency and reduce downtime. Smart Factory solution provides the necessary Manucturing Reports & Visualization to visualize the KPIs.
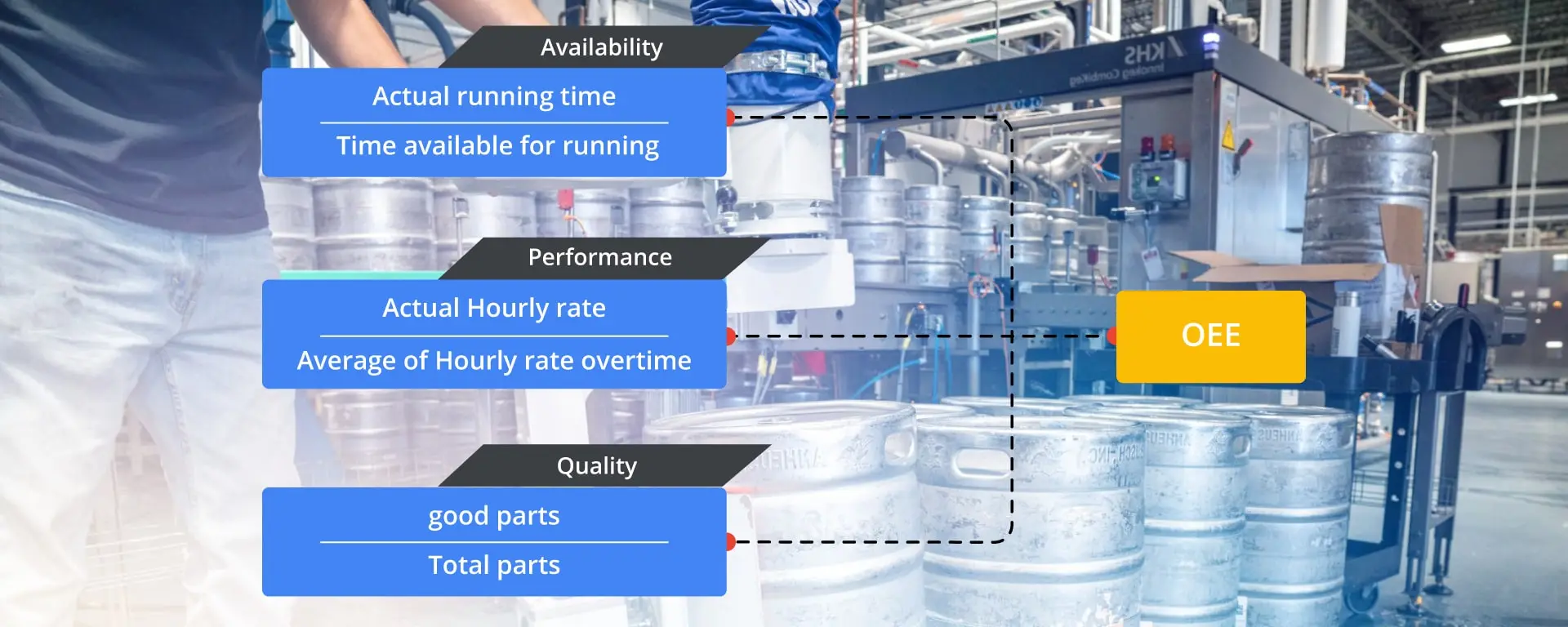
What is the OEE Formula?
The OEE formula of the continuous manufacturing is more like the discrete one. However the difference is the way in which the production is calculated. The meaurement of the output is in terms of volume ( litres or gallons ), weight ( KG or pounds) and length ( m or inches).
- Availability – The comparison of the time for which the machine is available for operation against the time for which the machine is actually running for production.
- Performance – Actual output versus what the machine should have produced for the time it is actually running.
- Quality – The total number of parts manufactured against the number of parts produced according to the client’s specifications ( at the right quality standards).
Availability = Runtime / Planned production time
Performance = (Ideal cycle time * Total count) / Runtime
Quality = Quantity of good parts / Total quantity made
OEE = Availabilty * Performance * Quality (* given in percentage*)
Batch Manufacturing
Batch process production is a way of producing things in predetermined groups or quantities over a set period of time. Batch might thus go through a succession of steps in a major manufacturing process to produce the desired final product. However, as a batch progresses, there will be a break between each stage. Batch production is utilised for some kinds of manufacturing that might require more modest measures of production at a time to ensure explicit quality norms or changes simultaneously. Batch process can handle different products which has similar properties. Industrial process like Heat Treatment, hardening, baking, debinding, sintering uses the batch process and has multiple stages where temperature, moisture and gas flows are controlled. connected to the next to maintain efficiency and reduce downtime Smart Factory solution provides the necessary Manucturing Reports & Visualization to visualize the KPIs. The Process Parameter monitoring for the Batch process is integral part of the Smart Factory solution.
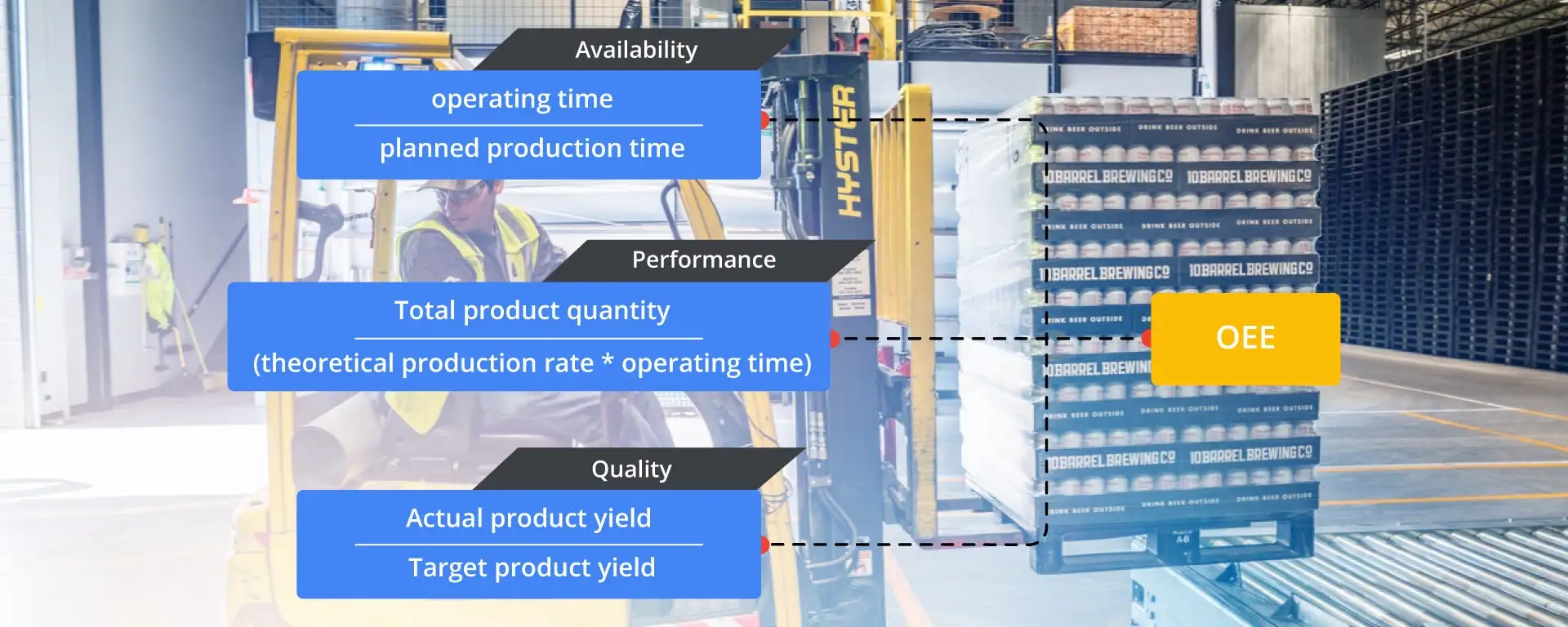
OEE Calculation
Machine Availability – It is the operating time divided by planned production time. In addition, the operating time is the difference between planned production time and downtime. The downtime of the machines is caused due to stoppage or setup or machine breakdown. The planned production time refers to the time between a batch being scheduled and time it goes to a running state. Generally it refers to the production time without any downtime. Hence the availability can be calculated as follows
Availability = operating time / planned production time
Operating time = Planned production time – Downtime
Planned production time = Batch duration – Scheduled time
Performance – In addition, the rate is essentially an ideal throughput for each process unit in terms of capacity over time.
Performance = Total product quantity / (theoretical production rate * operating time)
Product Quality - We can determine quality by dividing the actual product yield from target product yield.
Quality = Actual product yield / Target product yield
Repetitive Manufacturing
Repetitive manufacturing is the manufacturing shop floor process work in which products are delivered for rapid production flow. Continuous manufacture of the same product over a lengthy period of time is referred to as repetitive manufacturing. There is no end value for the quantity produced. It is predominantly utilized for production scenarios with high product, high repetition rates, and low product complexity. Some of the products produced in this process are Refridgerators, washing machines, automobiles, electonric goods, etc. These products mostly fall under the make to stock category. The manufacturing KPI charts derived out of the data acquired from the machines by the MES Software application will help understand the OEE of the shop floor.
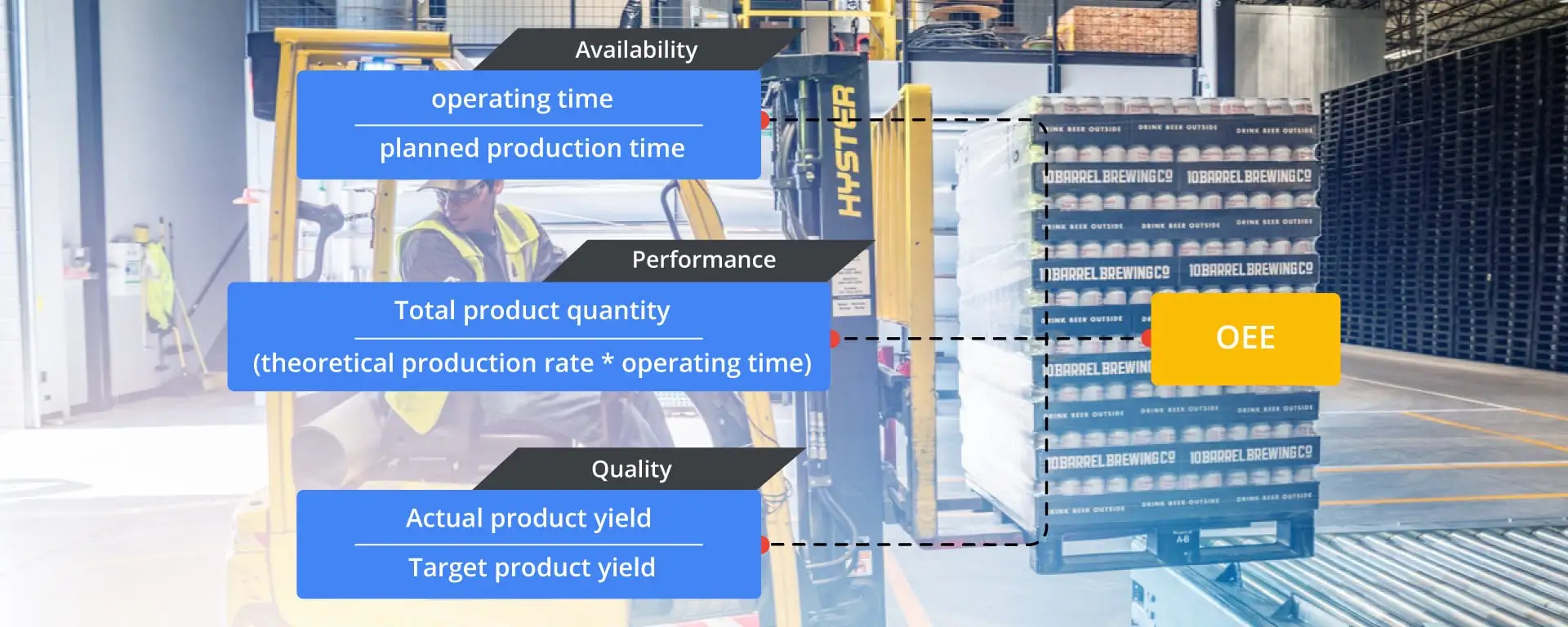
OEE Formula
Availability – Availability is the proportion of operating time and the planned production time that are available for production in the manufacturing process. The difference between the planned production time and the unplanned stop time is the operating time. The percentage of time a machine can actually manufacture parts compared to the total time it should take to produce parts.
Availability = Operating time / planned production time
Operating time = planned production time – unplanned stop time
Performance -The second part of OEE looks at the actual running speed of the plant or equipment against its predetermined working speed. The predetermined run speed is frequently referred to as ideal cycle time. Performance is the actual throughput of the plant during the time it ran, contrasted with the most extreme throughput that it might have accomplished running at the ideal cycle time. Performance losses are divided into two categories: micro stops and slow cycles.
Performance = (Total parts / operating time) / Ideal cycle time
Quality – The third component of OEE measures quality, essentially reflecting the proportion of production throughput that meets client specifications accurately on the first attempt. Quality losses fall into two classes: production rejects, and start-up rejects.
Quality = Sum of good parts / Total parts
Job Shop Manufacturing
A job shop is a type of manufacturing process that produces small batches of a wide range of unique products. Furthermore, this is concerned with customisation and limited production runs. The final products come produced in little groups (of varying quantities). Customers customize their orders to meet their particular necessities. This implies a business will deliver a small volume of products that are not normalized.
OEE Formula & Calculating OEE
Availability – The planned downtime factor refers to lapses in the schedule and allotted breaks. Some causes of downtime have a negative impact on OEE in the job shop, while others do not. For example, if a machine is down for an extended period of time, the operator may be unable to locate the necessary tools to set up the machine, which reduces OEE. However, if a machine is idle simply because it has no more scheduled work, it is still available if needed. As a result, depending on the situation, this may not have a negative impact on OEE.
Performance - In general, we need a standard “ideal” cycle time to calculate performance. But nothing is standard in the job shop. Instead of trying to apply a single ideal performance rating to each machine/part combination, we should only apply a unique ideal performance rating to each machine/part combination.
Quality – Quality can be defined as the proportion of good parts produced in relation to the total number of parts produced.
Hope this article provides a detailed information of how to do your OEE measurement for each production processes and will help you improve your manufacturing operations using an effective production monitoring system.
Digitally Track your OEE
Imrpove Operational Efficiency
Learn MES Software helps transform your shop-floor
